2.1.7. Planned Maintenance Design Guideline¶
This document describes how one can implement infrastructure maintenance in interaction with VNFM by utilizing the OPNFV Doctor project framework and to meet the set requirements. Document concentrates to OpenStack and VMs while the concept designed is generic for any payload or even different VIM. Admin tool should be also for controller and other cloud hardware, but that is not the main focus in OPNFV Doctor and should be defined better in the upstream implementation. Same goes for any more detailed work to be done.
2.1.7.1. Problem Description¶
Telco application need to know when infrastructure maintenance is going to happen in order to guarantee zero down time in its operation. It needs to be possible to make own actions to have application running on not affected resource or give guidance to admin actions like migration. More details are defined in requirement documentation: use cases, architecture and implementation.
2.1.7.2. Guidelines¶
Concepts used:
- event: Notification to rabbitmq with particular event type.
- state event: Notification to rabbitmq with particular event type including payload with variable defined for state.
- project event: Notification to rabbitmq that is meant for project. Single event type is used with different payload and state information.
- admin event: Notification to rabbitmq that is meant for admin or as for any infrastructure service. Single event type is used with different state information.
- rolling maintenance: Node by Node rolling maintenance and upgrade where a single node at a time will be maintained after a possible application payload is moved away from the node.
- project stands for application in OpenStack contents and both are used in this document. tenant is many times used for the same.
Infrastructure admin needs to make notification with two different event types. One is meant for admin and one for project. Notification payload can be consumed by application and admin by subscribing to corresponding event alarm trough alarming service like OpenStack AODH.
- Infrastructure admin needs to make a notification about infrastructure maintenance including all details that application needs in order to make a decisions upon his affected service. Alarm Payload can hold a link to infrastructure admin tool API for reply and for other possible information. There is many steps of communication between admin tool and application, thus the payload needed for the information passed is very similar. Because of this, the same event type can be used, but there can be a variable like state to tell application what is needed as action for each event. If a project have not subscribed to alarm, admin tool responsible for the maintenance will assume it can do maintenance operations without interaction with application on top of it.
- Infrastructure admin needs to make an event about infrastructure maintenance telling when the maintenance starts and another when it ends. This admin level event should include the host name. This could be consumed by any admin level infrastructure entity. In this document we consume this in Inspector that is in OPNFV Doctor project terms infrastructure entity responsible for automatic host fault management. Automated actions surely needs to be disabled during planned maintenance.
Before maintenance starts application needs to be able to make switch over for his ACT-STBY service affected, do operation to move service to not effected part of infrastructure or give a hint for admin operation like migration that can be automatically issued by admin tool according to agreed policy.
There should be at least one empty host compatible to host under maintenance in order to have a smooth rolling maintenance done. For this to be possible also down scaling the application instances should be possible.
Infrastructure admin should have a tool that is responsible for hosting a maintenance work flow session with needed APIs for admin and for applications. The Group of hosts in single maintenance session should always have the same physical capabilities, so the rolling maintenance can be guaranteed.
Flow diagram is meant to be as high level as possible. It currently does not try to be perfect, but to show the most important interfaces needed between VNFM and infrastructure admin. This can be seen e.g. as missing error handling that can be defined later on.
Flow diagram:
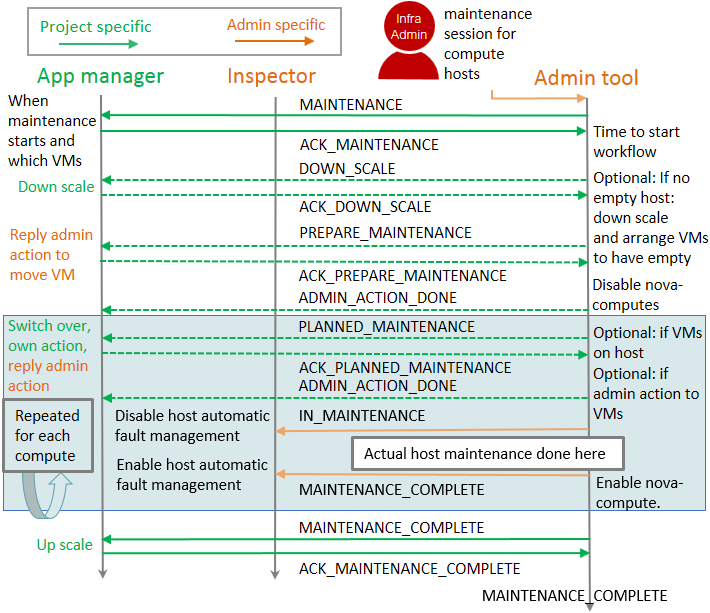
Flow diagram step by step:
Infrastructure admin makes a maintenance session to maintain and upgrade certain group of hardware. At least compute hardware in single session should be having same capabilities like the amount number of VCPUs to ensure the maintenance can be done node by node in rolling fashion. Maintenance session need to have a session_id that is a unique ID to be carried throughout all events and can be used in APIs needed when interacting with the session. Maintenance session needs to have knowledge about when maintenance will start and what capabilities the possible upgrade to infrastructure will bring to application payload on top of it. It will be matter of the implementation to define in more detail whether some more data is needed when creating a session or if it is defined in the admin tool configuration.
There can be several parallel maintenance sessions and a single session can include multiple projects payload. Typically maintenance session should include similar type of compute hardware, so you can guarantee moving of instances on top of them can work between the compute hosts.
State MAINTENANCE project event and reply ACK_MAINTENANCE. Immediately after a maintenance session is created, infrastructure admin tool will send a project specific ‘notification’ which application manager can consume by subscribing to AODH alarm for this event. As explained already earlier all `project event`s will only be sent in case the project subscribes to alarm and otherwise the interaction with application will simply not be done and operations could be forced.
The state MAINTENANCE event should at least include:
- session_id to reference correct maintenance session.
- state as MAINTENANCE to identify event action needed.
- instance_ids to tell project which of his instances will be affected by the maintenance. This might be a link to admin tool project specific API as AODH variables are limited to string of 255 character.
- reply_url for application to call admin tool project specific API to answer ACK_MAINTENANCE including the session_id.
- project_id to identify project.
- actions_at time stamp to indicate when maintenance work flow will start. ACK_MAINTENANCE reply is needed before that time.
- metadata to include key values pairs of a capabilities coming over the maintenance operation like ‘openstack_version’: ‘Queens’
Optional state DOWN_SCALE project event and reply ACK_DOWN_SCALE. When it is time to start the maintenance work flow as the time reaches the actions_at defined in previous state event, admin tool needs to check if there is already an empty compute host needed by the rolling maintenance. In case there is no empty host, admin tool can ask application to down scale by sending project specific DOWN_SCALE state event.
The state DOWN_SCALE event should at least include:
- session_id to reference correct maintenance session.
- state as DOWN_SCALE to identify event action needed.
- reply_url for application to call admin tool project specific API to answer ACK_DOWN_SCALE including the session_id.
- project_id to identify project.
- actions_at time stamp to indicate when is the last moment to send ACK_DOWN_SCALE. This means application can have time to finish some ongoing transactions before down scaling his instances. This guarantees a zero downtime for his service.
Optional state PREPARE_MAINTENANCE project event and reply ACK_PREPARE_MAINTENANCE. In case still after down scaling the applications there is still no empty compute host, admin tools needs to analyze the situation on compute host under maintenance. It needs to choose compute node that is now almost empty or has otherwise least critical instances running if possible, like looking if there is floating IPs. When compute host is chosen, a PREPARE_MAINTENANCE state event can be sent to projects having instances running on this host to migrate them to other compute hosts. It might also be possible to have another round of DOWN_SCALE state event if necessary, but this is not proposed here.
The state PREPARE_MAINTENANCE event should at least include:
- session_id to reference correct maintenance session.
- state as PREPARE_MAINTENANCE to identify event action needed.
- instance_ids to tell project which of his instances will be affected by the state event. This might be a link to admin tool project specific API as AODH variables are limited to string of 255 character.
- reply_url for application to call admin tool project specific API to answer ACK_PREPARE_MAINTENANCE including the session_id and instance_ids with list of key value pairs with key as instance_id and chosen action from allowed actions given via allowed_actions as value.
- project_id to identify project.
- actions_at time stamp to indicate when is the last moment to send ACK_PREPARE_MAINTENANCE. This means application can have time to finish some ongoing transactions within his instances and make possible switch over. This guarantees a zero downtime for his service.
- allowed_actions to tell what admin tool supports as action to move instances to another compute host. Typically a list like: [‘MIGRATE’, ‘LIVE_MIGRATE’]
Optional state INSTANCE_ACTION_DONE project event. In case admin tool needed to make action to move instance like migrating it to another compute host, this state event will be sent to tell the operation is complete.
The state INSTANCE_ACTION_DONE event should at least include:
- session_id to reference correct maintenance session.
- instance_ids to tell project which of his instance had the admin action done.
- project_id to identify project.
At this state it is guaranteed there is an empty compute host. It would be maintained first trough IN_MAINTENANCE and MAINTENANCE_COMPLETE steps, but following the flow chart PLANNED_MAINTENANCE will be explained next.
Optional state PLANNED_MAINTENANCE project event and reply ACK_PLANNED_MAINTENANCE. In case compute host to be maintained has instances, projects owning those should have this state event. When project receives this state event it knows instances moved to other compute host as resulting actions will now go to host that is already maintained. This means it might have new capabilities that project can take into use. This gives the project the possibility to upgrade his instances also to support new capabilities over the action chosen to move instances.
The state PLANNED_MAINTENANCE event should at least include:
- session_id to reference correct maintenance session.
- state as PLANNED_MAINTENANCE to identify event action needed.
- instance_ids to tell project which of his instances will be affected by the event. This might be a link to admin tool project specific API as AODH variables are limited to string of 255 character.
- reply_url for application to call admin tool project specific API to answer ACK_PLANNED_MAINTENANCE including the session_id and instance_ids with list of key value pairs with key as instance_id and chosen action from allowed actions given via allowed_actions as value.
- project_id to identify project.
- actions_at time stamp to indicate when is the last moment to send ACK_PLANNED_MAINTENANCE. This means application can have time to finish some ongoing transactions within his instances and make possible switch over. This guarantees a zero downtime for his service.
- allowed_actions to tell what admin tool supports as action to move instances to another compute host. Typically a list like: [‘MIGRATE’, ‘LIVE_MIGRATE’, ‘OWN_ACTION’] OWN_ACTION means that application may want to re-instantiate his instance perhaps to take into use the new capability coming over the infrastructure maintenance. Re-instantiated instance will go to already maintained host having the new capability.
- metadata to include key values pairs of a capabilities coming over the maintenance operation like ‘openstack_version’: ‘Queens’
State IN_MAINTENANCE and MAINTENANCE_COMPLETE admin event`s. Just before host goes to maintenance the IN_MAINTENANCE state event will be send to indicate host is entering to maintenance. Host is then taken out of production and can be powered off, replaced, or rebooted during the operation. During the maintenance and upgrade host might be moved to admin’s own host aggregate, so it can be tested to work before putting back to production. After maintenance is complete MAINTENANCE_COMPLETE state event will be sent to know host is back in use. Adding or removing of a host is yet not included in this concept, but can be addressed later.
The state IN_MAINTENANCE and MAINTENANCE_COMPLETE event should at least include:
- session_id to reference correct maintenance session.
- state as IN_MAINTENANCE or MAINTENANCE_COMPLETE to indicate host state.
- project_id to identify admin project needed by AODH alarm.
- host to indicate the host name.
State MAINTENANCE_COMPLETE project event and reply MAINTENANCE_COMPLETE_ACK. After all compute nodes in the maintenance session have gone trough maintenance operation this state event can be send to all projects that had instances running on any of those nodes. If there was a down scale done, now the application could up scale back to full operation.
- session_id to reference correct maintenance session.
- state as MAINTENANCE_COMPLETE to identify event action needed.
- instance_ids to tell project which of his instances are currently running on hosts maintained in this maintenance session. This might be a link to admin tool project specific API as AODH variables are limited to string of 255 character.
- reply_url for application to call admin tool project specific API to answer ACK_MAINTENANCE including the session_id.
- project_id to identify project.
- actions_at time stamp to indicate when maintenance work flow will start.
- metadata to include key values pairs of a capabilities coming over the maintenance operation like ‘openstack_version’: ‘Queens’
At the end admin tool maintenance session can enter to MAINTENANCE_COMPLETE state and session can be removed.
2.1.7.3. Benefits¶
- Application is guaranteed zero downtime as it is aware of the maintenance action affecting its payload. The application is made aware of the maintenance time window to make sure it can prepare for it.
- Application gets to know new capabilities over infrastructure maintenance and upgrade and can utilize those (like do its own upgrade)
- Any application supporting the interaction being defined could be running on top of the same infrastructure provider. No vendor lock-in for application.
- Any infrastructure component can be aware of host(s) under maintenance via `admin event`s about host state. No vendor lock-in for infrastructure components.
- Generic messaging making it possible to use same concept in different type of clouds and application payloads. instance_ids will uniquely identify any type of instance and similar notification payload can be used regardless we are in OpenStack. Work flow just need to support different cloud infrastructure management to support different cloud.
- No additional hardware is needed during maintenance operations as down- and up-scaling can be supported for the applications. Optional, if no extensive spare capacity is available for the maintenance - as typically the case in Telco environments.
- Parallel maintenance sessions for different group of hardware. Same session should include hardware with same capabilities to guarantee rolling maintenance actions.
- Multi-tenancy support. Project specific messaging about maintenance.
2.1.7.4. Future considerations¶
- Pluggable architecture for infrastructure admin tool to handle different clouds and payloads.
- Pluggable architecture to handle specific maintenance/upgrade cases like OpenStack upgrade between specific versions or admin testing before giving host back to production.
- Support for user specific details need to be taken into account in admin side actions (e.g. run a script, …).
- (Re-)Use existing implementations like Mistral for work flows.
- Scaling hardware resources. Allow critical application to be scaled at the same time in controlled fashion or retire application.
2.1.7.4.1. POC¶
There was a Maintenance POC demo ‘How to gain VNF zero down-time during Infrastructure Maintenance and Upgrade’ in the OCP and ONS summit March 2018. Similar concept is also being made as OPNFV Doctor project new test case scenario.
